Using Welding Techniques to improve 3D Metal Printing
A research team led by Dr. Sang-woo Song, Dr. Chan-kyu Kim, Dr. Kang-myung Seo at the Department of Joining Technology of the Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS), a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT, has developed a foundational technology for controlling the volume of molten metal in the process of 3D printing metal using welding techniques.
They achieved this through collaborative research with a research team led by Professor Young-tae Cho and Professor Seok Kim of the Department of Mechanical engineering at Changwon National University, and a research team led by Dr. Dae-won Cho of Busan Machinery Research Center at the Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials. As a result, they have successfully developed a metal 3D printing pen technology that can continuously print metal in a three-dimensional space with freedom.
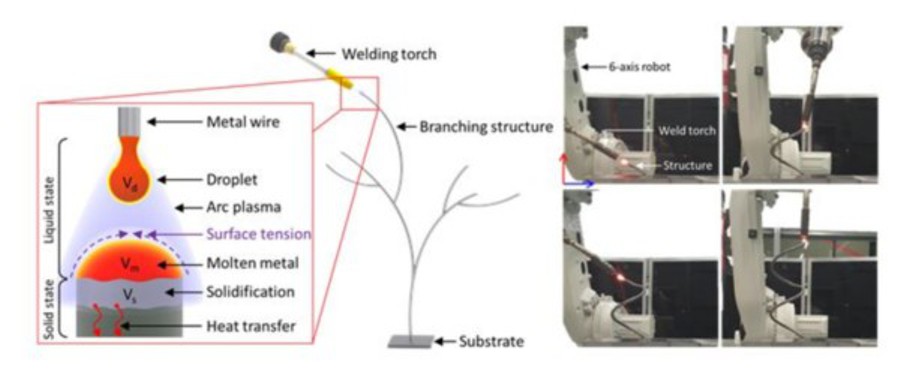
The metal 3D printing pen technology developed by the research team has the advantage of being able to freely and continuously print metal with freedom in the direction of the welding torch’s movement in 3D space. Compared to conventional metal 3D printing using lasers, the equipment construction cost is low, and additive manufacturing can be performed quickly using commercially available welding materials, making it more economical.
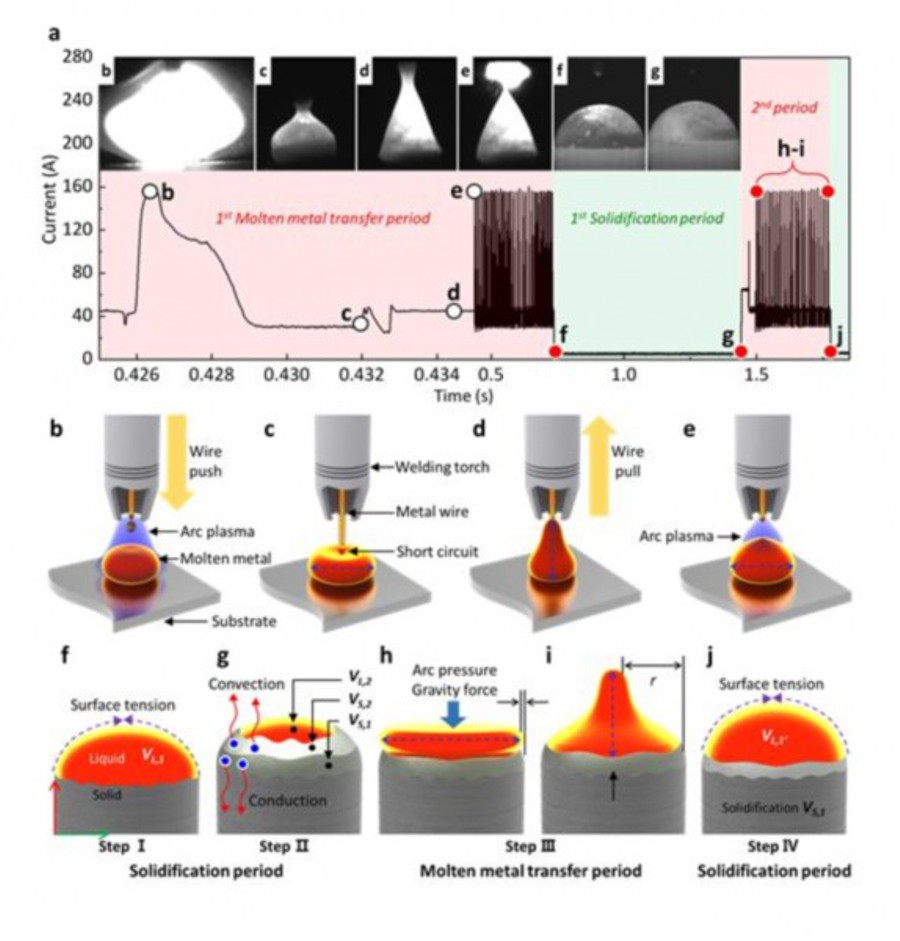
Metal additive manufacturing using welding techniques has limitations in realizing complex structures because it is a limited process of building one layer at a time. This is because subsequent layers are laminated after complete solidification preventing the molten metal from flowing down. Due to this, there is a disadvantage in that a cooling time is required and the conditions that can be laminated are limited to specific examples.
To solve this problem, the research team performed computer analysis to calculate and precisely control the surface tension of the molten metal and the solidified volume according to convection / conduction. Additionally, they developed a technology that can perform metal additive manufacturing in all conditions, including horizontal, vertical, inclined, and overhead positions.
By continuously laminating the metal in the liquid phase before it fully solidifies, the manufacturing time is shortened, there is no boundary between layers, and it forms a dense microstructure with excellent mechanical properties.
In the case of ductility, 24.5% improvement compared to the existing WAAM (Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing) process, based on Inconel 625 (WAAM: welding and additive manufacturing (AM) of wire-type materials using an arc heat source).
As of 2021, the size of the 3D printer market at home and abroad is KRW 82.1 billion and USD 2.1 billion, respectively, with annual average growth rates of 10.5% and 20%. This research achievement is expected to give vitality to the manufacturing industry by preoccupying technological superiority in the field of metal additive manufacturing and manufacturing high-value-added machines and parts using it.
“We added 3D free-form additive manufacturing to the continuous additive manufacturing process, which was considered impossible in the existing metal additive manufacturing process,” said Sang-woo Song, principal researcher at KIMS, who is in charge of the research. He continued, “Like the existing 3D printing technology using polymers, it is possible to easily manufacture complex structures using existing metal welding materials, suggesting a new paradigm for the manufacturing industry.”
This research result was carried out as a project of ‘Development of Multi-metallic Layer Materials for Multi-purpose Micro Modular Reactor’ by the Korea Institute of Materials Science with the support of the Ministry of Science and ICT. In addition, the research results were selected as a cover paper in the February issue of Advanced Science (IF=17.521), a world-renowned academic journal. Currently, the research team is continuing follow-up research for additive manufacturing of high-value-added machinery and parts in the nuclear power plant and defence industries.






























