Injection Moulding vs 3D Printing: The Realm of Modern Manufacturing
The manufacturing world is evolving rapidly, with technologies like injection moulding and 3D printing at the forefront.
Both these techniques have revolutionized production processes, but each serves different needs and applications. Injection moulding, a traditional method, is known for its efficiency in high-volume production, while 3D printing, a relatively modern innovation, offers unparalleled flexibility in design.
Understanding their historical development and fundamental differences is crucial for anyone navigating the manufacturing landscape.
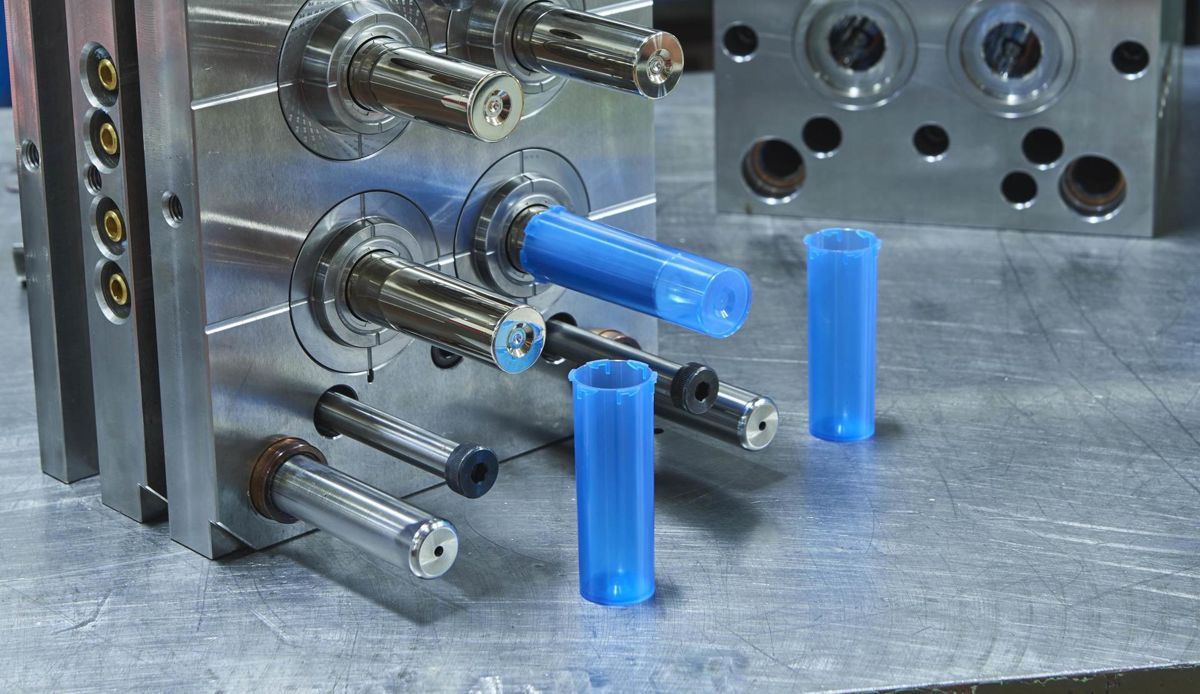

What is Injection Moulding?
Injection moulding is a time-honored manufacturing process primarily used for mass production. It involves injecting molten material into a mould to create parts with high precision and repeatability. In the industry, commonly used materials for injection molding include plastics such as polystyrene, polyethylene, and ABS. Recently, the use of polymer blends in injection molding has emerged as a latest trend.
How Does Injection Moulding Work?
The Process Unveiled: In injection moulding, the journey from raw material to finished product involves several key stages:
- Melting the material
- Injecting it into a mould
- Cooling and solidifying
- Ejecting the final product
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file. It involves adding material layer by layer, which allows for complex designs that are often impossible with traditional methods.
This technology uses a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, and ceramics.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM, the most common type of 3D printing, involves melting a thermoplastic filament and extruding it to form layers.
- Stereolithography (SLA): SLA uses a laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic in a process that offers high detail and smooth finishes.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): In SLS, a laser sinters powdered material to create strong and durable parts.
For your specific needs, you can choose 3D printer by Raise3D.
How Does 3D Printing Work?
Exploring the Additive Approach
The 3D printing process encompasses several stages:
- Designing the 3D model
- Slicing the model into layers
- Sequentially adding material layer by layer
- Post-processing for refinement
Comparing Costs: Injection Moulding vs 3D Printing
Analyzing Financial Implications: When comparing costs, injection moulding generally has higher initial expenses due to mould design and production but becomes cost-effective in large volumes. Conversely, 3D printing has lower start-up costs and is more economical for small batches and prototyping.
Quality and Precision: Injection Moulding vs 3D Printing
Assessing Output Excellence: Injection moulding is renowned for its precision and consistency, especially in producing identical parts. On the other hand, 3D printing offers exceptional detail and complexity in design, albeit sometimes at a lower surface finish quality.
Speed and Efficiency: Which is Faster?
Time as a Critical Factor: Injection moulding’s speed is unmatched in high-volume production, while 3D printing leads in rapid prototyping and short production runs.
Flexibility and Customization: Which Offers More?
Embracing Design Creativity: The crown for customization flexibility undoubtedly goes to 3D printing, allowing for on-the-fly design changes and complex geometries.
Material Selection and Properties: Injection Moulding vs 3D Printing
Diverse Material Universe: Both technologies offer a wide range of materials, but the choice depends on the desired properties like strength, durability, and flexibility. Injection moulding materials are generally more uniform and predictable, while 3D printing offers innovative material combinations and composites.
Production Volume: Which Technology is Best Suited for What Scale?
Volume Versus Versatility: Injection moulding is the go-to for high-volume production due to its speed and lower per-unit cost, while 3D printing excels in low-volume, high-variety scenarios.
Environmental Impact: A Comparative Analysis
Weighing the Sustainability Factor: Both technologies present unique environmental challenges. Injection moulding can lead to material waste in the form of sprues and runners, while 3D printing’s energy consumption and material limitations are areas of concern.
Limitations and Challenges of Injection Moulding
Confronting the Constraints: Injection moulding, while efficient, faces challenges like high initial costs, design limitations for complex geometries, and longer lead times for mould production.
Limitations and Challenges of 3D Printing
Navigating the New Terrain: 3D printing, despite its flexibility, grapples with issues like slower production rates for large quantities, lower strength in some materials, and a need for post-processing.
Future Trends and Advancements in Injection Moulding and 3D Printing
Forecasting Manufacturing Evolution: Emerging trends in both technologies include increased automation, advancements in materials, and integration with digital technologies like AI and IoT. The future will likely see a more significant blending of these techniques as their unique advantages are combined in hybrid manufacturing approaches.
Case Studies: Successful Applications of Injection Moulding and 3D Printing
Real-World Success Stories: Examining case studies from industries like healthcare, automotive, and aerospace reveals how both technologies have been used to drive innovation, reduce costs, and speed up product development.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider
Deciding on the Ideal Manufacturing Path: Selecting between injection moulding and 3D printing involves considering factors such as production volume, cost, design complexity, material requirements, and time constraints.

Conclusion
The choice between injection moulding and 3D printing depends on specific project requirements. Each technology has unique strengths and limitations, making them suitable for different applications.
Understanding these will guide manufacturers and designers in making informed decisions, ensuring the optimal use of each method for their specific needs.