AI innovations to revolutionise Wastewater Treatment
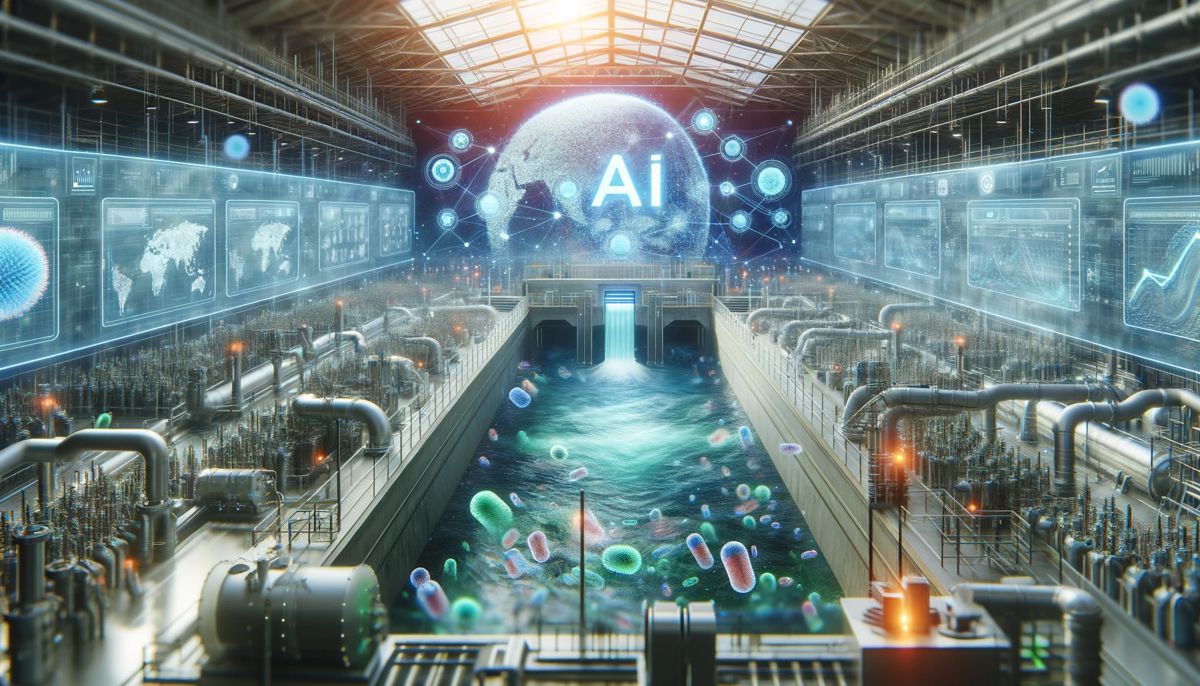
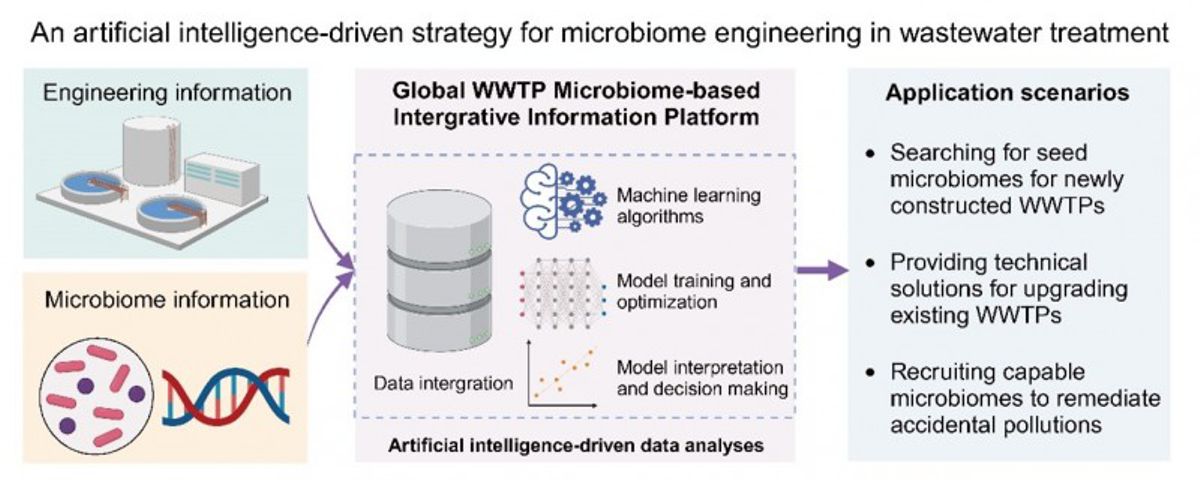
In a recent study published online 18 December 2023 in the journal Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, scientists from Peking University introduced a ground-breaking Global WWTP Microbiome-based Integrative Information Platform to address the escalating complexities of pollutants and inadequacies in traditional WWTPs.
This platform, inspired by the advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), is poised to revolutionize the field of environmental engineering and microbiome research.
The innovative platform harnesses extensive microbiome and engineering data from WWTPs around the world. By utilizing advanced AI-driven tools, it analyses the data to identify optimal microbiomes, upgrade facilities, and effectively respond to pollution accidents.
This AI-driven platform strives for a stronger, faster, and globally integrated wastewater treatment solution, thereby enhancing WWTPs’ indispensable role in pollution control and environmental sustainability.
Highlights
- A “Global WWTP Microbiome-based Integrative Information Platform” is proposed.
- The Platform employs AI-driven modelling and analysing for WWTP-relevant parties.
- The Platform aims to enhance the biodegradation efficiency of pollutants on Earth.
- The Platform will be of significance for our human society and natural environment.
“The Global WWTP Microbiome-based Integrative Information Platform is not just a technological advancement; it’s a paradigm shift in how we cope with environmental challenges,” stated Donghui Wen, a leading figure in environmental engineering. “By harnessing the power of AI and global data, we’re moving from mere experience-based methods to an era of informed intelligence.”
The implications of this platform are vast. It is expected to significantly enhance the performance of WWTPs in pollution control, contributing to a more harmonious and healthy future for human society and the natural environment. It supports multidisciplinary research, documents microbial evolution, advances wastewater-based epidemiology, and enhances global resource sharing.






























