Shedding light on Semiconductors for Solar Fuels
Scientists are advancing the use of semiconductors to convert sunlight into renewable energy. In solar cells, semiconductors convert sunlight into electricity. When brought into direct contact with water, semiconductors can instead use sunlight to convert water into hydrogen, a carbon-free fuel.
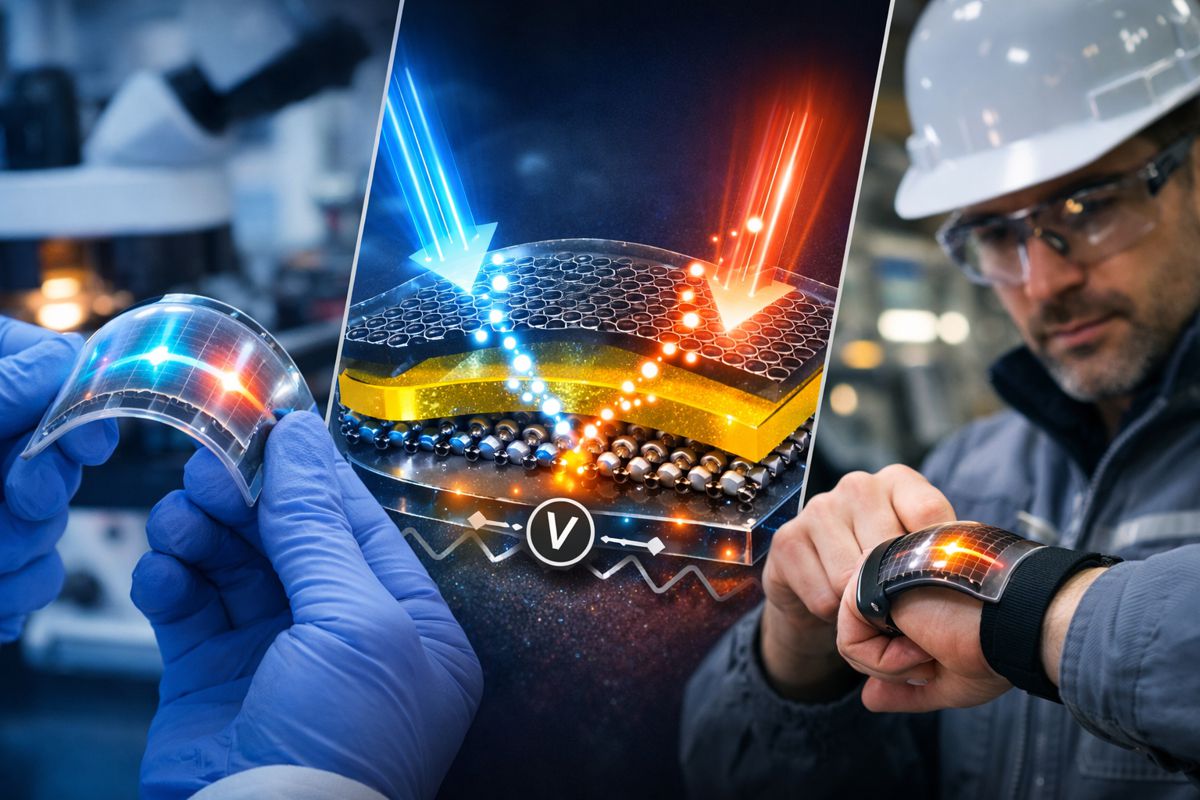
The energy output from the semiconductor is given by its photovoltage. Now researchers have developed a new technique to measure this photovoltage quantitatively. Measuring the photovoltage is essential to finding the best conditions to make fuel from sunlight and water.
The Impact
Researchers can easily measure the electric energy output of solar cells using wires that connect the cell and a measuring device. However, this energy output is difficult to measure in solar fuel electrodes that are in contact with water.
This is because pure water is not electrically conductive, preventing researchers from observing the photovoltage. Here, researchers show that the photovoltage of such solar fuel electrodes can be measured in a contactless way.
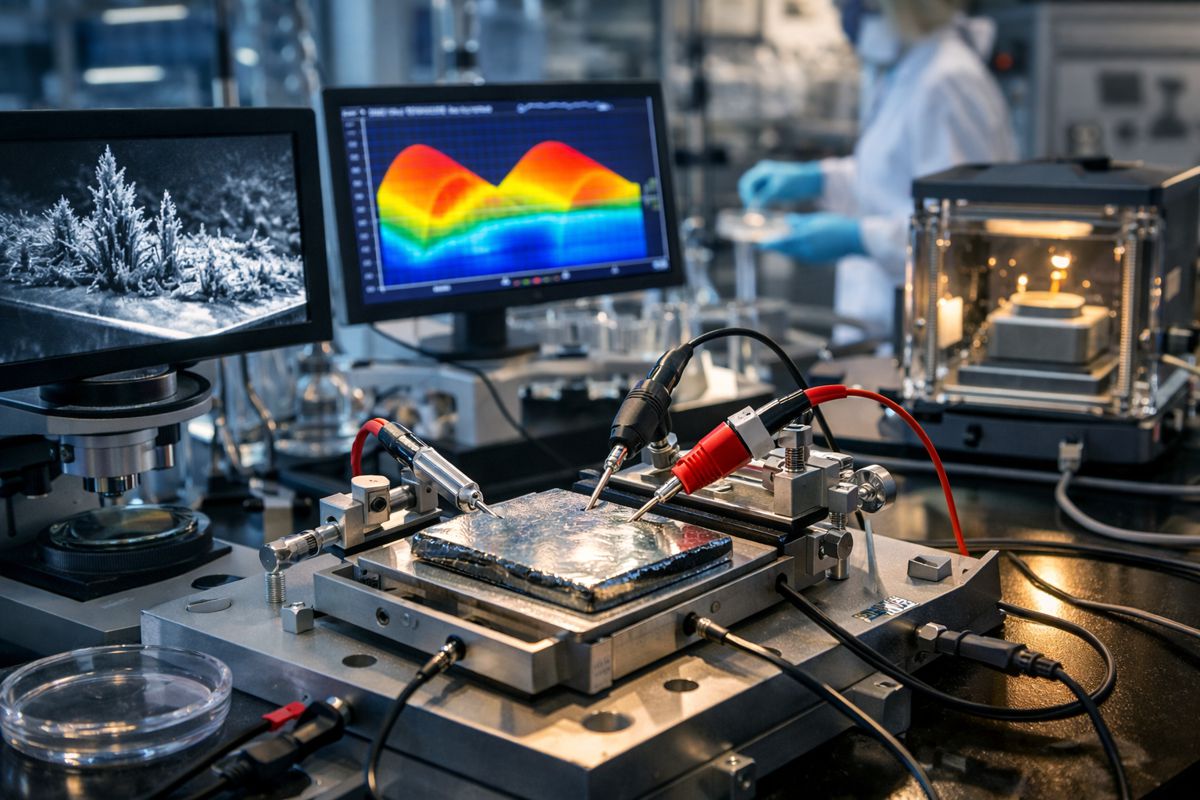
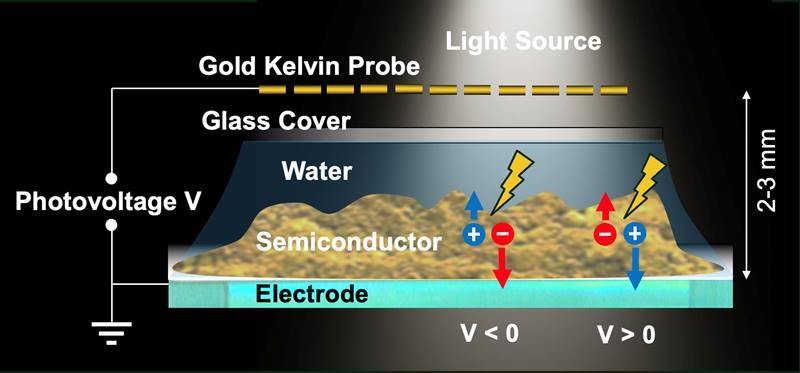
They did so by using a so-called gold Kelvin probe that hovers over the illuminated device and picks up the information through space.
Summary
In this research, scientists from the University of California, Davis and Martin Luther University in Germany conducted contactless photovoltage measurements on bismuth vanadate, a semiconductor for water oxidation, and on copper gallium selenide, a semiconductor for hydrogen generation from water.
They covered the semiconductors with water solutions and a glass microscopy slide and placed the slide underneath the Kelvin probe.
The researchers found that the photovoltage depends not only on the semiconductor, but also on the color of the light (the photon energy), the light intensity, and the chemical properties of the water solution. This information allows scientists to identify the best conditions for the direct conversion of solar energy into hydrogen and other fuels.
Funding
The measurements were supported by the Department of Energy Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences.