5 Manufacturing Innovations in the Automotive Industry
The automotive industry has experienced countless technological revolutions. New manufacturing methods and innovations, such as the assembly line or electric power sources, have led to explosive transformations in the field.
These advancements change the mentality surrounding design, assembly, and maintenance throughout all stages of a vehicle’s lifetime. They affect aspects ranging from road performance to environmental impact.
The latest automotive trends focus on autonomous driving systems, robotic manufacturing techniques, and EV sustainability. Each of these contributes to shaping a more efficient, safer, and convenient experience for owners and manufacturers.

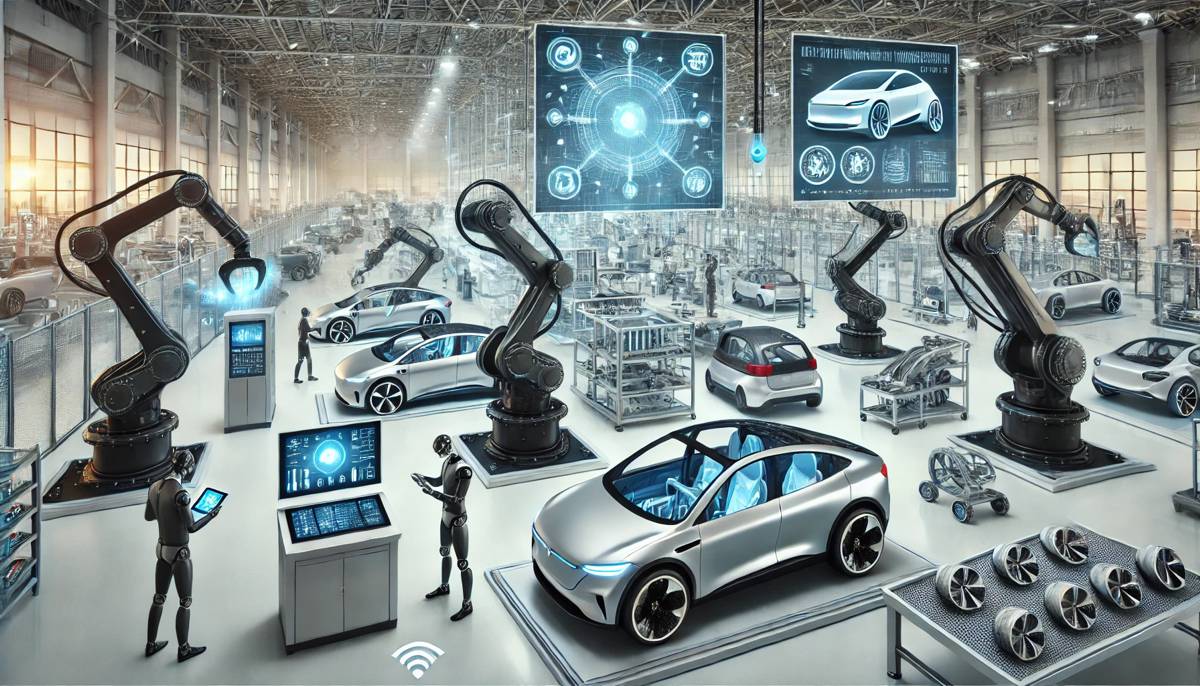
Advanced Robotics in Assembly Lines
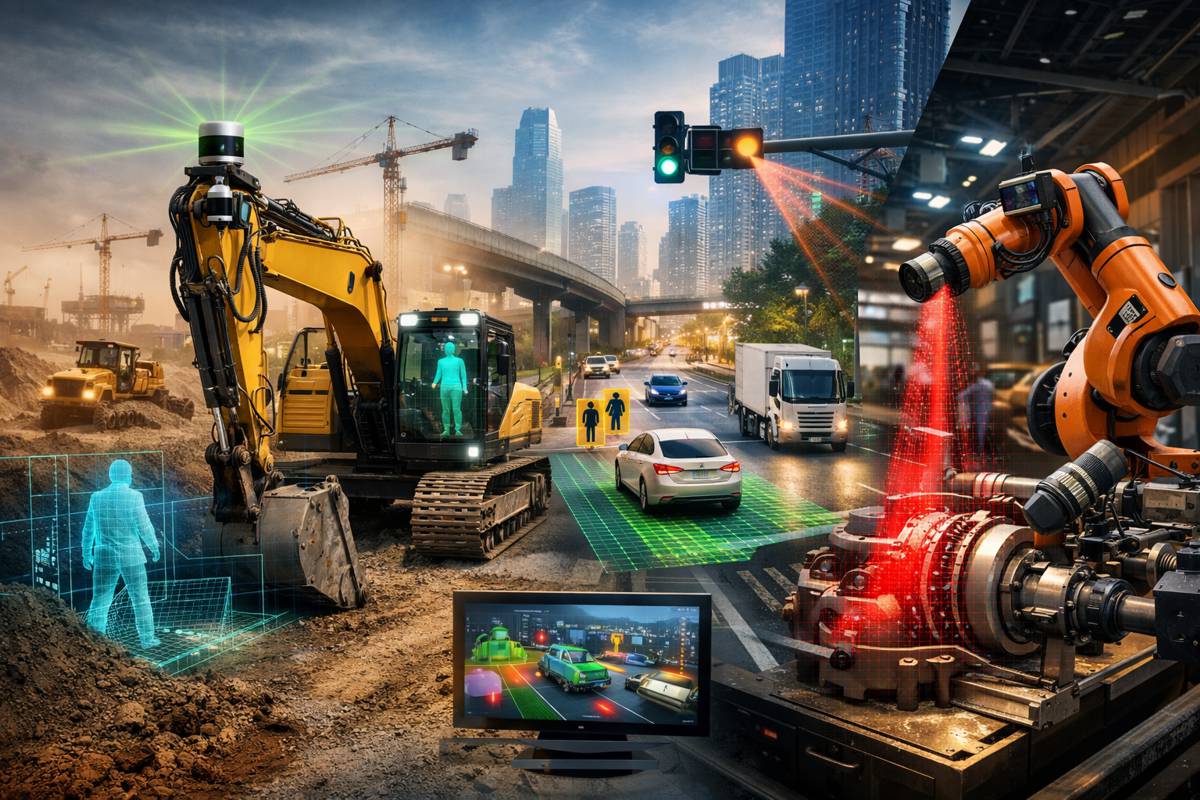
Advanced robotics has vastly improved the efficiency of automotive assembly lines. Traditional assembly lines are human-powered, increasing injury risk and reducing precision. Collaborative robots (cobots) are the latest technology designed to operate cooperatively with humans.
Cobots take over tasks that are overly repetitive or too precise for human operators. These robots are compact and less expensive than large industrial machinery, helping medium-sized manufacturers compete in small-batch environments.
Additionally, cobots are uniquely suited to the switch to more electronic systems in vehicles. These systems call for greater accuracy during assembly. Sensors and computing hardware must be consistently placed, a task better handled by robots.
This reallocation of labour allows employees to focus on creative and solution-oriented issues on the production line. Cobots are also safer than industrial robots. They are equipped with sensors that can detect accidental contact and automatically shut down.

Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing is an industrial version of 3D printing, referring to automotive part production through layering material in precise patterns. This novel manufacturing method permits more intricate and customized designs.
It has applications throughout the manufacturing process, from prototyping to creating the final components. Additionally, there are several versions of additive manufacturing for different materials, such as polymers, ceramics, and various metals.
Additive manufacturing makes it quicker and more cost-effective for businesses to procure vehicle parts. Engineers can quickly test designs with cheaper materials and adjust performance at a fraction of the cost of traditional iteration.
The computer-driven design process also gives engineers greater precision, allowing them to create more efficient, durable, and lightweight parts. These advantages lead to better fuel economy and battery life compared to traditionally manufactured vehicles.
Electric Cars and Sustainable Manufacturing
Electric vehicles (EVs) are one of the most transformative trends in the automotive industry. They appeal to consumers’ growing interest in responsible sustainability and environmental protections. Many governments have also enacted legislation rewarding greener transportation.
EVs are more environmentally friendly due to their reliance on renewable energy. However, consumers are seeking to promote businesses with a positive environmental footprint in all aspects, not just in the final product. This means that manufacturers must pivot their entire production process to succeed.
A common green choice is integrating recycled materials to minimize waste. Some companies reuse plastics from water bottles and packaging in the bumpers and trim. Scrap metal can also be melted down and repurposed into engine components.
In EVs, lightweight options like carbon fibre and advanced polymers are the trending material choices. These materials reduce the vehicle’s weight and increase driving range. Equally important is the choice of battery technology—lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries being the primary options. Lithium-ion batteries, known for their high energy density and lighter weight, are the preferred choice for most EVs, providing longer ranges and faster charging capabilities. In contrast, lead-acid batteries, though more affordable and easier to recycle, have lower energy density and a shorter lifespan, making them less suitable for modern EVs where range and efficiency are key.

Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Production
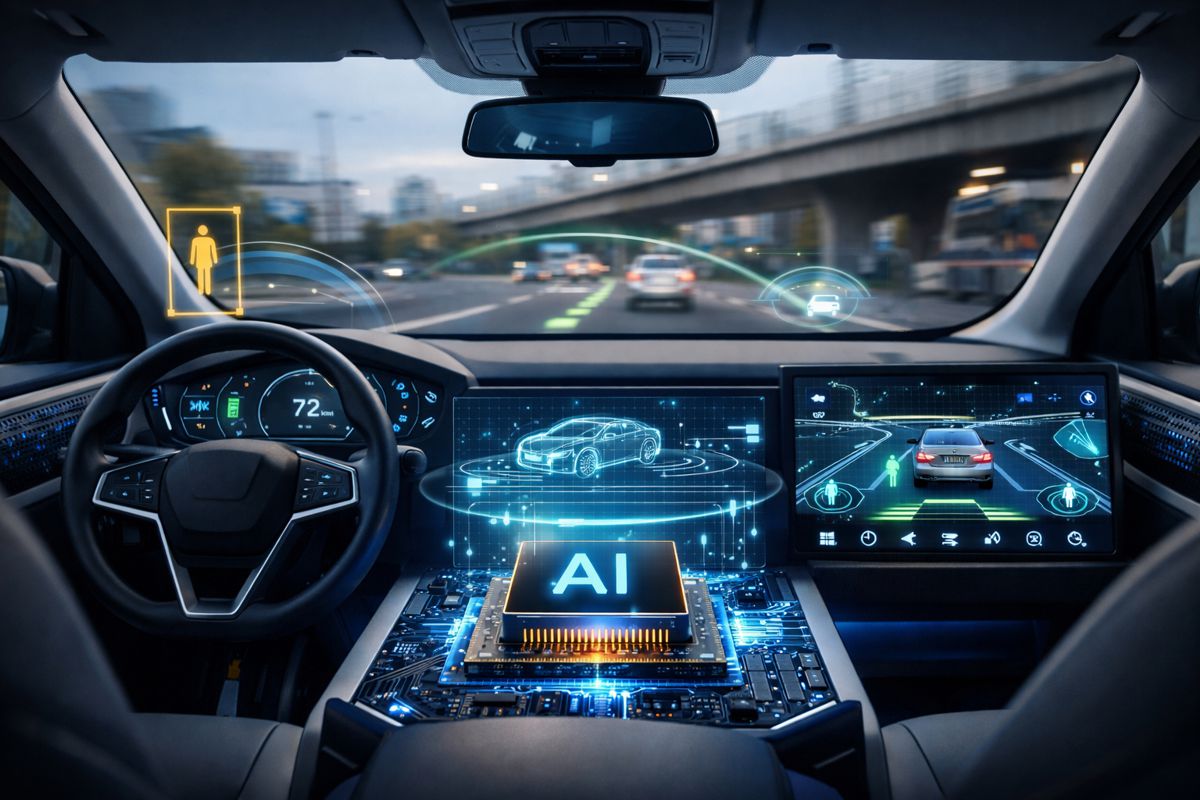
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are becoming increasingly important in efficient production lines. These technologies optimize supply management, enhance quality control, and allow for quick decision-making.
One of the most essential cogs in successful manufacturing is consistently performing equipment. AI analyses vast amounts of data in real-time, including machinery performance. This data can track wear and tear, predict potential malfunctions, and give factories crucial preparation time.
By identifying potential issues before they lead to equipment downtime, manufacturers can schedule maintenance more effectively, reducing costs and preventing costly production delays.
AI also plays a central role in self-driving cars outside the production line. Information from cameras, sensors, and driver habits teaches vehicles how to behave in particular situations without requiring constant programming and updates.

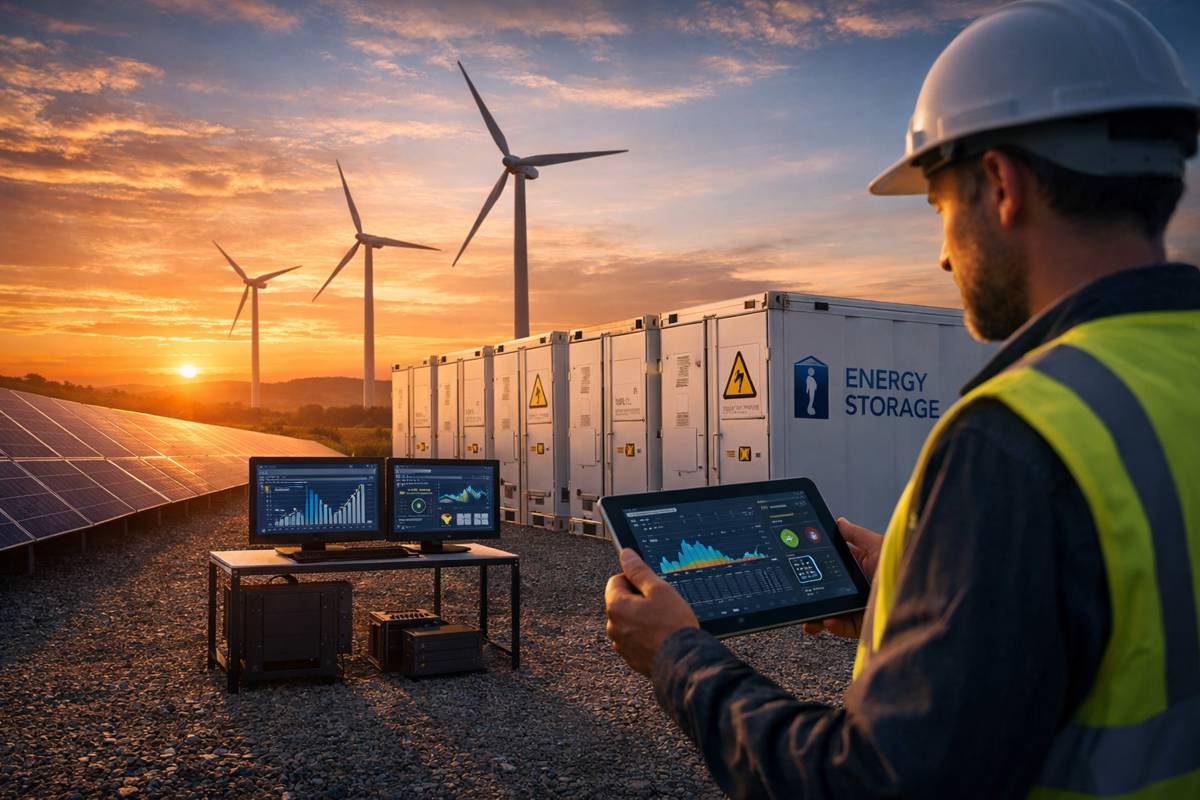
Smart Factories and the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things refers to internationally shared data networks created by internet-connected devices. Smartphones, laptops, thermostats, and many other devices collect and share information on users and general performance.
Businesses tap into this network to improve their products and target their desired customer base. Smart factories, powered by this massive database, collect information from parts, machinery, and factory sensors to improve operations.
Readings from machinery performance and energy consumption reduce production costs, increase safety, and help companies reach their sustainability goals.
Additionally, the IoT can identify component defects by analysing performance in other vehicles using the same parts. This allows manufacturers to learn from others’ mistakes and address the problem in the production process.
Smart factories will become even more autonomous, with AI and IoT systems working in tandem to manage the holistic production process with minimal human intervention. These technological advancements are revolutionizing the automotive industry, enabling manufacturers to build more efficient, sustainable, and advanced vehicles than ever before.





























