Metal Recovery from Copper Slag turns Waste into Wealth
Copper smelting is a major source of copper production, generating significant amounts of slag. In 2022, China produced over 11,000 kilotons of refined copper, leading to 2.2 to 3 tons of slag per ton of copper produced.
This slag contains valuable metals like copper (0.5%–6%), lead (0.2%–0.6%), and zinc (1%–5.5%), which are often not recovered, resulting in resource waste and environmental hazards from leaked toxic ions.
A study released on 19 January 2024, in Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China detailing a novel method for the recovery of copper, lead, and zinc from copper smelting slag using a sulfurization-reduction approach. This innovation represents a significant stride in metallurgical waste management, with potential impacts on both industry practices and environmental sustainability.
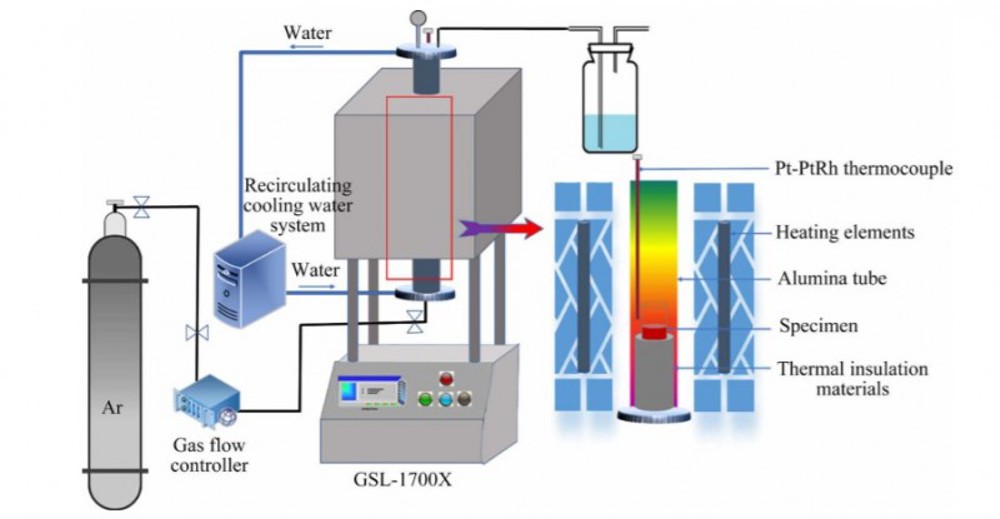
The research from Central South University presents a significant advance in metal recycling technology, particularly for copper, lead, and zinc recovery from copper smelting slag. Using pyrite as a sulfurizing agent, this novel sulfurization-reduction technique facilitates the efficient extraction of these metals. The team’s rigorous approach, combining thermodynamic analysis with practical laboratory experiments, has led to high recovery rates, achieving nearly 98% for copper and zinc and about 90% for lead.
This method is not only effective in reclaiming valuable metals from what was previously considered waste but also plays a crucial role in environmental protection. By significantly reducing the harmful residues in the leftover slag, this method contributes to a more sustainable approach to waste management in the metallurgical industry. It suggests a shift towards more eco-friendly practices, emphasizing the importance of both economic viability and environmental responsibility in resource recovery processes.
Qing-hua Tian, a lead researcher, states: “This sulfurization-reduction method not only recovers valuable metals efficiently but also significantly reduces the environmental footprint of copper smelting.”
This research opens up new possibilities for the future of metal recovery, recovering valuable metals and reducing environmental harm. It presents significant implications for the metallurgical industry, especially in countries with high copper production, aligning industrial practices with the growing need for environmental sustainability.






























