Oman Expands National Wastewater Capacity With Landmark PPP Projects
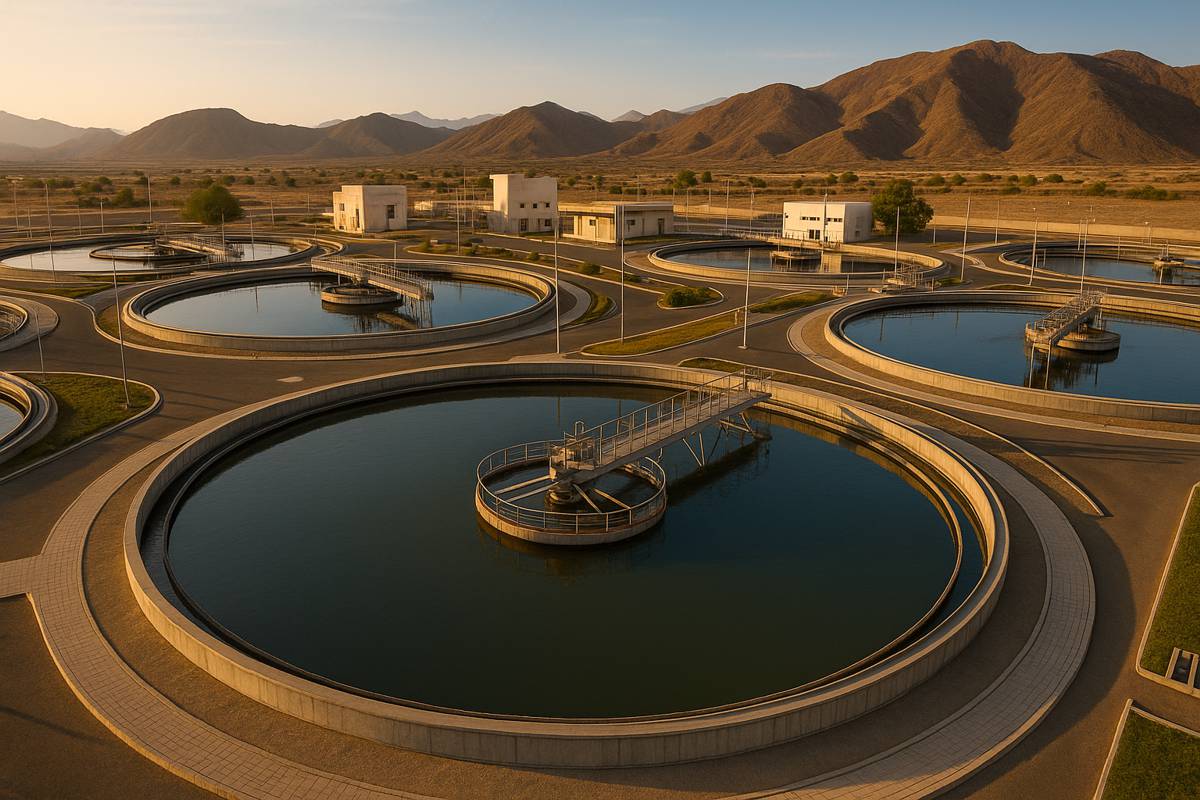
Oman’s wastewater landscape is entering a pivotal new phase as Nama Water Services (NWS), part of the wider Nama Group, launches an international public-private partnership tender for two major sewage treatment plant projects. The initiative brings the long-term development and operation of the Al Ansab STP Phase III and the Al Amerat STP Phase II to market, signalling a decisive move to expand national capacity and improve environmental resilience.
The tender introduces a Build-Own-Operate-Transfer model, placing private partners at the centre of design, financing, construction, and long-term operations. By doing so, Oman aims to accelerate investment while ensuring both existing and new assets are managed to modern standards. According to NWS, the procurement process is structured to attract local, regional, and global consortia capable of delivering high-quality wastewater solutions.
The Significance Of Capacity Expansion
The scale of the proposed expansions highlights the country’s shifting demographic profile and its continued urban growth. The Al Ansab STP is set for an uplift of roughly 82,000 cubic metres per day, raising its total capacity from 125,000 to around 207,000 cubic metres per day. This significant enhancement reflects Al Ansab’s role as one of Oman’s largest and most critical wastewater hubs.
Meanwhile, the Al Amerat STP is expected to increase its daily capacity from 18,000 to approximately 54,000 cubic metres. Tripling capacity at this site is seen as essential in meeting rising demand from residential, commercial, and industrial users within the rapidly developing Amerat region.
Together, these expansions represent one of the most substantial upgrades to Oman’s wastewater network in recent years. The projects are designed not only to meet present-day requirements but to anticipate shifts in population distribution and demand over the coming decades.
A Closer Look At The BOOT Framework
Public-private partnerships have been steadily shaping infrastructure development across the Gulf, and Oman has emerged as an active participant in PPP reforms. The BOOT model selected for these sewage treatment facilities is designed to distribute responsibility and risk between the public and private sectors.
Under this framework, the selected consortium will own and operate the facilities for a defined term, offering the potential for private investors to achieve predictable long-term returns. At the end of the concession, assets will be transferred back to NWS. International lenders typically view BOOT schemes favourably due to their clear asset lifecycle and reliable performance structures.
In Oman, PPPs have gained momentum through the establishment of regulatory processes that bring greater transparency to procurement. Recent water and wastewater projects have demonstrated the government’s commitment to using private-sector expertise to improve operational efficiency across utilities.
Strengthening Environmental And Economic Outcomes
Expanding wastewater treatment capacity has considerable environmental implications. Modern sewage treatment plants reduce pollution loads, support groundwater protection, and help safeguard fragile marine ecosystems. In rapidly urbanising countries like Oman, enhanced wastewater infrastructure forms a foundation for sustainability and climate resilience.
The expanded facilities at Al Ansab and Al Amerat are expected to incorporate advanced treatment technologies, enabling the reuse of treated effluent in agriculture, district cooling, and industry. Recycled water has become an essential resource in the Gulf, offering an alternative supply in regions facing water scarcity.
Wastewater management also feeds into Oman’s broader economic strategy. Improved sanitation systems increase investor confidence, particularly in industrial zones, tourism developments, and logistics corridors. By boosting long-term infrastructure reliability, the projects support job creation and stimulate local contracting and supply chains.
The Tendering Process And Requirements
Nama Water Services has opened registration for interested parties to access the Request for Qualification. Consortia must submit company details, key contact personnel, and communication information to the dedicated tender email. Upon confirmation, participants will receive instructions for downloading the RFQ documentation and any subsequent updates.
Applications must be submitted by 16 December 2025 at 2:30 pm Gulf Standard Time. Queries and requests for clarification may be directed to the dedicated PPP tender address.
The RFQ stage will allow NWS to shortlist bidders with proven technical, financial, and operational credentials. Following prequalification, selected consortia will advance to the Request for Proposals stage, where detailed engineering, financial models, and operational frameworks will be submitted for evaluation.
Leveraging Global Expertise For National Benefit
International participation is expected to be significant due to Oman’s favourable investment environment and track record in BOOT utilities. Construction firms and operators specialising in wastewater engineering are likely to take strong interest in the tender. The government’s continued alignment with global best practice in environmental standards further increases the appeal of the projects.
For domestic companies, the tender presents opportunities to form joint ventures and develop long-term partnerships with global players. Capacity building, sector upskilling, and local supply chain development remain important components of Oman’s infrastructure vision.
National Sustainable Development
These wastewater projects arrive at an important juncture for Oman, where sustainable development across utilities is seen as a cornerstone of national progress. Expanded and upgraded treatment facilities will serve growing communities, support industrial diversification, and help preserve scarce natural resources.
As Nama Water Services progresses through the procurement process, the success of the Al Ansab and Al Amerat expansions will depend on the combined strengths of engineering expertise, financial robustness, and a long-term commitment to operational excellence.