Urban canyons a high tech road block for Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles could face signal black-out caused by “urban canyons” in cities across the world due to the continued growth of skyscrapers and urban infrastructure, according to Oxbotica – a global leader in autonomous vehicle software.
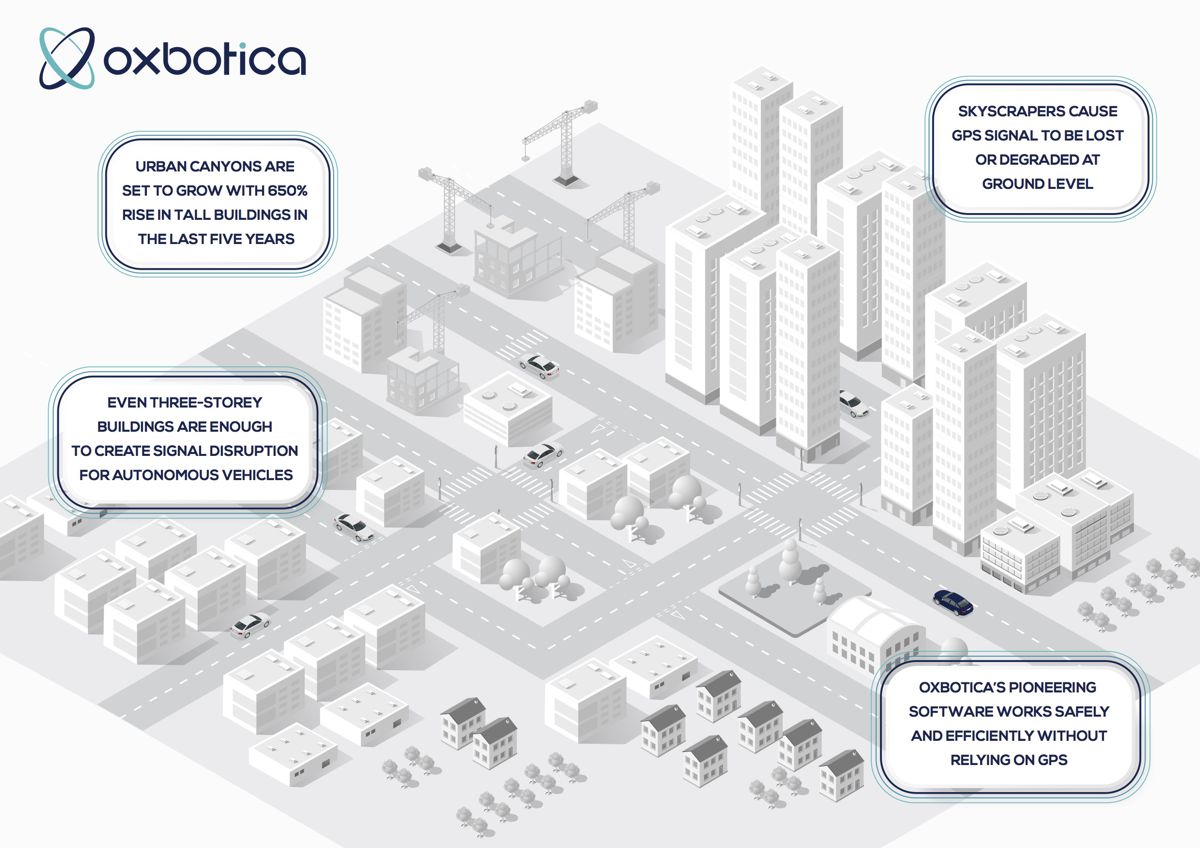
Urban canyons are formed when a street is densely populated by tall buildings on both sides. This can cause the GPS signal at ground level to be degraded or lost, either through satellite signals being obscured, or through multipath effects: a phenomenon where radio waves bounce off surroundings and form multiple signal paths.
The number of tall buildings (above 200m) has risen by 650% in the last five years and with this number set to increase again by up to 20% in 2020, the frequency of urban canyons in our society is only set to grow.
Interruption of GPS signals, through connection drops or multipath degradation, has potential safety and operational implications for autonomous vehicle systems that rely heavily on satellite-based navigation.

Even a standard three-storey building is enough to create signal disruption at ground level. And the problem is worse at higher latitudes where satellites tend to be lower in the sky. If no suitable fallbacks are in place, this can affect autonomous vehicles in these environments, including mass transit shuttles, buses, city delivery vehicles and cars.
However, canyons are not the only issue with GPS dependency. Sunspots formed during the sun’s 11-year magnetic field cycle cause marked changes in the solar wind. This impacts the upper atmosphere which can in turn interfere with GPS satellites. The solution is to use a mix of radars, cameras and lasers to navigate and localise rather than relying solely on GPS.
Paul Newman, CTO & Founder at Oxbotica, said: “My first job was in the maritime positioning industry where we were providing alternatives to GPS positioning systems for ships and oil rigs in the Gulf Of Mexico two sun-cycles ago, now I’m in conversations about the same problem hitting autonomous vehicles on our roads, and in our mines – on top of being in any number of canyons.

“While it is harder to figure out your location using vehicle-mounted sensors rather than being told it by GPS, the rewards are many. Entirely new commercial opportunities open up – working underground is no different to a high street, an autonomous shuttle is no different to a haulage truck in a mine. This is a powerful concept and underpins our Universal Autonomy software platform.”
Oxbotica’s world-leading autonomy technology is able to work independently of any external infrastructure, allowing continuous localisation and safe control of its vehicles – even without a GPS signal. Oxbotica’s localisation system is not reliant on a single sensor modality, and instead uses a mixture of radar, laser and vision sensing to deliver autonomous operation in a vast range of settings, on any vehicle platform, under any conditions.
This pioneering technology has already operated in a range of environments without access to GPS, for example in mines and quarries, inside warehouses, and in ‘urban canyons’ across Europe, Asia and America. It uses the same software to run autonomous vehicles, in any environment, without needing to change a single line of code.
Ben Upcroft, VP of Technology at Oxbotica, said: “There are so many urban canyons and GPS ‘blind spots’ across our towns, cities and countryside, that we can’t rely on GPS for accurate navigation. While this may pose a problem for some autonomous vehicles, our software is designed to mitigate this and is able to work independently of a GPS signal, helping us to bring autonomy to any vehicle in any environment – this is the central focus of our Universal Autonomy vision.”






























